In the age of digital transformation, accurate geospatial data is more critical than ever. From urban planning to environmental monitoring, modern mapping technologies have revolutionized the way we understand and interact with our world. Central to this revolution is GNSS navigation, a technology that has been instrumental in unlocking precision and enabling new possibilities in mapping and location-based services.
What is GNSS Navigation?
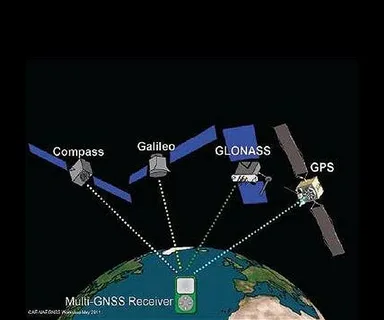
GNSS, or Global Navigation Satellite System, refers to a constellation of satellites that provide autonomous geo-spatial positioning worldwide. Systems such as the American GPS, Russian GLONASS, European Galileo, and Chinese BeiDou are all part of this global network. GNSS navigation allows users to determine their exact location (latitude, longitude, and altitude) with remarkable accuracy.
The Need for Precision in Modern Mapping
Mapping has evolved far beyond traditional paper maps. Today’s applications demand high precision—whether it’s for land surveying, autonomous vehicles, agriculture, or disaster management. Slight inaccuracies can lead to costly errors, inefficient resource allocation, and safety hazards. Here, unlocking precision through GNSS navigation is the key to success.
How GNSS Navigation Enhances Mapping Accuracy
GNSS navigation provides precise location data by triangulating signals from multiple satellites. This data enables:
- Real-time positioning: Instant updates allow dynamic mapping and tracking.
- Sub-meter accuracy: Advanced GNSS techniques, such as Real-Time Kinematic (RTK), achieve centimeter-level precision.
- Integration with GIS: Combining GNSS data with Geographic Information Systems (GIS) enhances spatial analysis and decision-making.
By leveraging GNSS navigation, modern mapping systems can generate accurate topographic maps, monitor infrastructure, and facilitate smart city initiatives with unprecedented detail.
Applications Benefiting from GNSS-Driven Precision
Many industries rely on GNSS navigation for enhanced mapping accuracy, including:
- Agriculture: Precision farming uses GNSS to optimize planting, irrigation, and harvesting.
- Transportation: Autonomous vehicles depend on accurate GNSS data for navigation and safety.
- Environmental Monitoring: Tracking changes in landscapes, forests, and waterways.
- Urban Planning: Designing efficient infrastructure and utilities.
Each of these applications highlights the transformative role of GNSS navigation in unlocking precision in their respective fields.
Challenges and Future Prospects
While GNSS navigation has drastically improved mapping precision, challenges remain, such as signal interference, multipath errors, and limited satellite visibility in urban canyons. Research continues to enhance GNSS technologies and integrate complementary systems like inertial navigation and AI.
The future of mapping lies in further unlocking precision through hybrid systems that combine GNSS with other sensors, delivering seamless and reliable spatial data even in challenging environments.
Conclusion
The phrase “Unlocking Precision: The Role of GNSS Navigation in Modern Mapping” encapsulates the critical importance of satellite-based positioning technology in today’s geospatial landscape. By providing unparalleled accuracy, real-time data, and broad applicability, GNSS navigation continues to redefine the boundaries of modern mapping, enabling smarter decisions and a more connected world.